|
POTASSIUM DICHROMATE |
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 7778-50-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 231-906-6 | |
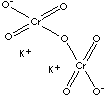
| FORMULA | Cr2K2O7 | |
| MOL WT. | 294.17 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 25 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Potassium dichromate (VI); Potassium bichromate; | |
| Kaliumdichromat; Dicromato de potasio; Dichromate de potassium; Bichromate of potash; Dichromic acid, dipotassium salt; Ddipotassium Dichromate; Chromic acid, dipotassium salt; Iopezite; | ||
|
SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | yellow to red crystals | |
| MELTING POINT | 398 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
500 C (Decomposes) |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 2.676 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
4.90 g/ml |
|
| pH |
4.0 (1.0% Sol.) |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 4; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 2; Special Hazard: OX | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Chromium (symbol Cr and atomic
number 24) occurs
in the oxidation states 0, +2, +3, and +6 states. Element (0) and divalent chromium,
however, are unstable. Chromium (0) immediately produce
a thin oxide layer. Divalent chromium is easily oxidized to the
trivalent form in air. The trivalent and hexavalent oxidation
states are important in industry, which exit in their divalent anions called
chromate and dichromate respectively and an chromic anhydride
form called chromium trioxide (CrO3)
and chromic oxide (Cr2O3).
In industrial, chromium trioxide is called chromic acid.
The principal uses of chromium are in the metallurgical
processing of ferrochromium and other metallurgical products to impart corrosion resistance,
chiefly stainless steel. There are applications in chrome plating, anodizing
aluminium, and refractory processing of chrome brick. When combined with oxygen together
other metallic elements such as lead and potassium,
it forms various inorganic pigments. Chromium is used
in chemical processing to
produce chromic acid and chromates. Chromates are strong oxidants which will produce
many organic and inorganic
materials and used in the purification of chemicals. Chromates are used as rust and corrosion inhibitors
in diesel engines. Dichromate is converted to
chromic sulfate for tanning of leather. Chromates and dichromates are used as pigments in paints
and in dyeing. Chrome colors include black, red, orange, green,
and yellow. Chromate salts contain the chromate ion, CrO4-2,
and have an intense yellow color. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate
ion, Cr2O7-2, and have an intense orange
color. Chromates are used as
mordant in dyeing cloth.
Potassium dichromate, also called red potassium chromate, is a bright yellowish-red crystals melting point at 396 C, decomposes at 500 C. Sodium dichromate is a red to orange deliquescent crystals melts at 320C. Sodium dichromate undergoes hydration when heated at 105C. They are soluble in water, insoluble in alcohol. Sodium and potassium dichromates are widely used as sources of other chromium compounds including chromic acid. Dichromates are power oxidizing agents which find applications in:
In biological field, potassium dichromate is used as a fixative for used for conservation of tissue sections. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
yellow to red crystals | |
| PURITY | 99.0% min | |
|
WATER INSOLUBLES |
0.02% max |
|
| SULPHATES | 0.04% max | |
| CHLORIDES |
0.02% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in Bag , 20mts in Container | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: I) | |
| UN NO. | 3086 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: T+ N, Risk Phrases: 46-49-46-21-25-26-37/38-41-43-50/53, Safety Phrases: 53-45-60-61 | ||